Hair loss is a concern that affects millions around the world. It can be alarming to notice increased shedding, especially when it seems to happen at certain times of the year. Many wonder if hair loss is seasonal — does your hair really shed more during particular seasons? And if so, what causes this pattern? At ZMD Hair, we’ve helped countless clients navigate the ups and downs of hair health and understand how natural cycles influence hair loss and regrowth.
In this comprehensive blog, we’ll explore the science behind seasonal hair shedding, how your hair growth cycle responds to environmental changes, and practical ways to protect and maintain your hair’s health year-round.
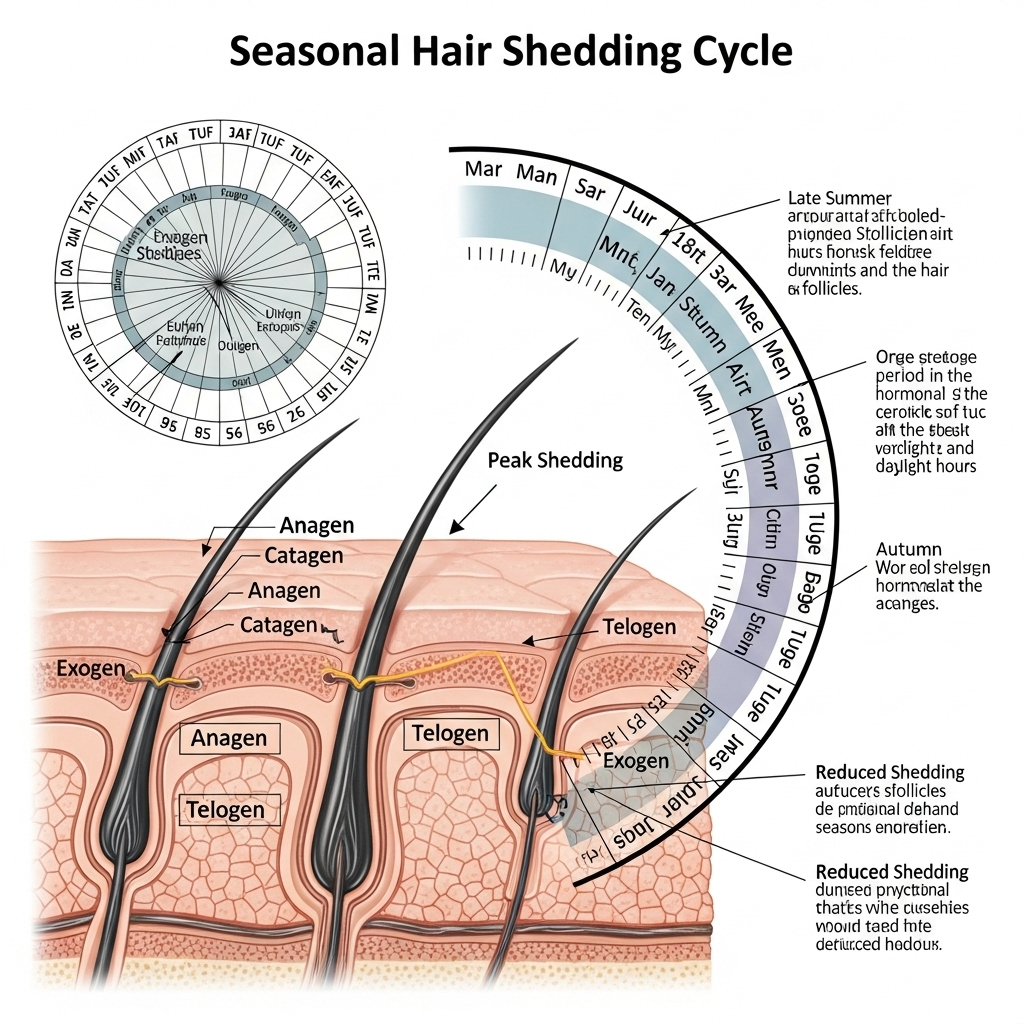
The Basics: How Hair Grows and Sheds
Before diving into seasonality, it’s important to understand how hair naturally grows and sheds. Hair follicles follow a cycle made up of three main phases:
- Anagen (Growth Phase): This phase lasts 2-7 years, during which hair actively grows. Approximately 85-90% of scalp hair is in this phase at any time.
- Catagen (Transition Phase): A brief 2-3 week phase where hair growth slows and follicles shrink.
- Telogen (Resting/Shedding Phase): Lasting about 3 months, hair follicles rest and eventually shed the old hair, making way for new hair to grow.
This cycle is continuous, ensuring constant renewal of hair strands. On average, losing about 50-100 hairs per day is normal.
Is Hair Loss Really Seasonal?
Many people report experiencing more hair shedding during certain times of the year, commonly in late summer and early fall. This observation is supported by several studies that confirm hair loss does indeed have a seasonal pattern.
The Science Behind Seasonal Hair Shedding
Research indicates that hair follicles may synchronize their shedding phase based on environmental cues, such as daylight length and temperature changes. This means a larger portion of hair follicles enter the telogen phase simultaneously during specific seasons, leading to noticeable shedding.
Several theories explain this:
- Evolutionary Adaptation: Human hair shedding patterns may be an inherited trait from ancestors who needed thicker hair in cold seasons and lighter coverage during warmer months. Seasonal shedding would optimize hair density according to climate.
- Melatonin Regulation: Changes in daylight influence melatonin production, a hormone that affects hair growth cycles. Variations in melatonin levels across seasons may trigger synchronized hair shedding.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature and humidity impact scalp health and hair follicle activity, which may cause slight fluctuations in hair growth and shedding rates.
What Do Studies Show?
Scientific studies corroborate the seasonal nature of hair loss:
- A 1991 study published in The British Journal of Dermatology observed a peak in hair shedding among participants during autumn.
- Additional studies suggest hair follicles enter the resting phase en masse during late summer or early fall, resulting in increased shedding shortly after.
- Seasonal shedding appears less prominent in tropical regions near the equator, where daylight hours and temperatures are more consistent year-round.
These studies show that seasonal hair loss is a natural physiological process for many people.
How Much Shedding Is Normal?
Seasonal shedding usually results in a temporary increase in daily hair loss — sometimes two to three times the normal amount. So, losing 100 to 300 hairs a day during peak shedding seasons can be normal.
The shedding period generally lasts several weeks to a couple of months, after which hair growth normalizes and lost hairs are replaced.
When Is Shedding a Cause for Concern?
Not all hair loss is seasonal or normal. It’s important to differentiate between natural seasonal shedding and conditions requiring professional care.
Signs that your hair loss may be abnormal include:
- Persistent thinning lasting longer than a few months
- Visible bald patches or receding hairlines
- Scalp itching, redness, or inflammation
- Family history of male or female pattern baldness
- Sudden, excessive shedding unrelated to seasons
If you experience these symptoms, a consultation with a hair specialist is recommended.
How to Support Your Hair Through Seasonal Changes
Managing hair health proactively helps minimize the impact of seasonal shedding. Here are some tips:
Nourish Your Hair from Within
A diet rich in protein, vitamins (especially biotin, vitamins A, C, D, and E), minerals like zinc and iron, and omega-3 fatty acids supports strong follicles and healthy hair growth.
Manage Stress
Stress disrupts hair cycles and can worsen shedding. Regular exercise, meditation, and quality sleep help regulate stress hormones and protect hair.
Gentle Hair Care
Use mild, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners. Avoid harsh chemicals, excessive heat styling, and tight hairstyles that cause tension and breakage.
Scalp Care
Massaging your scalp daily boosts circulation and follicle stimulation. Consider using nourishing oils or treatments that strengthen hair roots.
Protect from Environmental Damage
Extreme sun exposure, pollution, and dry air can weaken hair. Wearing hats, using UV-protectant sprays, and keeping hair hydrated are effective strategies.
Treatments to Combat Excessive Shedding
If seasonal shedding feels overwhelming or is combined with other hair loss factors, treatments can help:
- Topical Minoxidil: FDA-approved for androgenetic alopecia, it promotes follicle health and extends the growth phase.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Uses your own blood’s growth factors to stimulate follicles and improve scalp environment.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Non-invasive light treatments increase blood flow and cellular activity in follicles.
- Nutritional Supplements: Specific vitamins and minerals formulated for hair health can support regrowth.
At ZMD Hair, we provide customized treatment plans combining these options based on individual needs and hair loss patterns.
Why Professional Guidance Matters
Seasonal shedding is natural but can be complicated by underlying issues like hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, or medical conditions. Professional evaluation ensures accurate diagnosis and personalized care.
Our team at ZMD Hair specializes in identifying the causes of hair loss and designing effective, evidence-based treatment plans to restore your hair and confidence.
Conclusion: Embrace the Cycle and Care for Your Hair Year-Round
Hair shedding varies naturally throughout the year, with seasonal peaks that reflect your body’s biological rhythms and environmental influences. While this increased shedding can be alarming, understanding it as a normal process helps ease concerns.
With the right care—nutritional support, gentle styling, scalp health focus, and, when needed, medical treatments—you can maintain healthy hair through every season.
If you’re worried about hair loss or want professional advice tailored to your situation, contact ZMD Hair today. Our experts are ready to guide you on a personalized journey to fuller, stronger hair.
Don’t let seasonal shedding catch you off guard. Take control of your hair health now. Schedule a consultation with ZMD Hair and start your transformation today.